from __future__ import annotations
from typing import Any
import numexpr as ne
import numpy as np
from attrs import (
define,
field,
fields,
)
from numpy import pi
from floris.core import (
BaseModel,
Farm,
FlowField,
Grid,
Turbine,
)
from floris.utilities import cosd, sind
NUM_EPS = fields(BaseModel).NUM_EPS.default
[docs]
@define
class GaussVelocityDeflection(BaseModel):
"""
The Gauss deflection model is a blend of the models described in
:cite:`gdm-bastankhah2016experimental` and :cite:`gdm-King2019Controls` for
calculating the deflection field in turbine wakes.
parameter_dictionary (dict): Model-specific parameters.
Default values are used when a parameter is not included
in `parameter_dictionary`. Possible key-value pairs include:
- **ka** (*float*): Parameter used to determine the linear
relationship between the turbulence intensity and the
width of the Gaussian wake shape.
- **kb** (*float*): Parameter used to determine the linear
relationship between the turbulence intensity and the
width of the Gaussian wake shape.
- **alpha** (*float*): Parameter that determines the
dependence of the downstream boundary between the near
wake and far wake region on the turbulence intensity.
- **beta** (*float*): Parameter that determines the
dependence of the downstream boundary between the near
wake and far wake region on the turbine's induction
factor.
- **ad** (*float*): Additional tuning parameter to modify
the wake deflection with a lateral offset.
Defaults to 0.
- **bd** (*float*): Additional tuning parameter to modify
the wake deflection with a lateral offset.
Defaults to 0.
- **dm** (*float*): Additional tuning parameter to scale
the amount of wake deflection. Defaults to 1.0
- **use_secondary_steering** (*bool*): Flag to use
secondary steering on the wake velocity using methods
developed in [2].
- **eps_gain** (*float*): Tuning value for calculating
the V- and W-component velocities using methods
developed in [7].
TODO: Believe this should be removed, need to verify.
See property on super-class for more details.
References:
.. bibliography:: /references.bib
:style: unsrt
:filter: docname in docnames
:keyprefix: gdm-
"""
ad: float = field(converter=float, default=0.0)
bd: float = field(converter=float, default=0.0)
alpha: float = field(converter=float, default=0.58)
beta: float = field(converter=float, default=0.077)
ka: float = field(converter=float, default=0.38)
kb: float = field(converter=float, default=0.004)
dm: float = field(converter=float, default=1.0)
eps_gain: float = field(converter=float, default=0.2)
use_secondary_steering: bool = field(converter=bool, default=True)
[docs]
def prepare_function(
self,
grid: Grid,
flow_field: FlowField,
) -> dict[str, Any]:
kwargs = {
"x": grid.x_sorted,
"y": grid.y_sorted,
"z": grid.z_sorted,
"freestream_velocity": flow_field.u_initial_sorted,
"wind_veer": flow_field.wind_veer,
}
return kwargs
# @profile
[docs]
def function(
self,
x_i: np.ndarray,
y_i: np.ndarray,
yaw_i: np.ndarray,
turbulence_intensity_i: np.ndarray,
ct_i: np.ndarray,
rotor_diameter_i: float,
*,
x: np.ndarray,
y: np.ndarray,
z: np.ndarray,
freestream_velocity: np.ndarray,
wind_veer: float,
):
"""
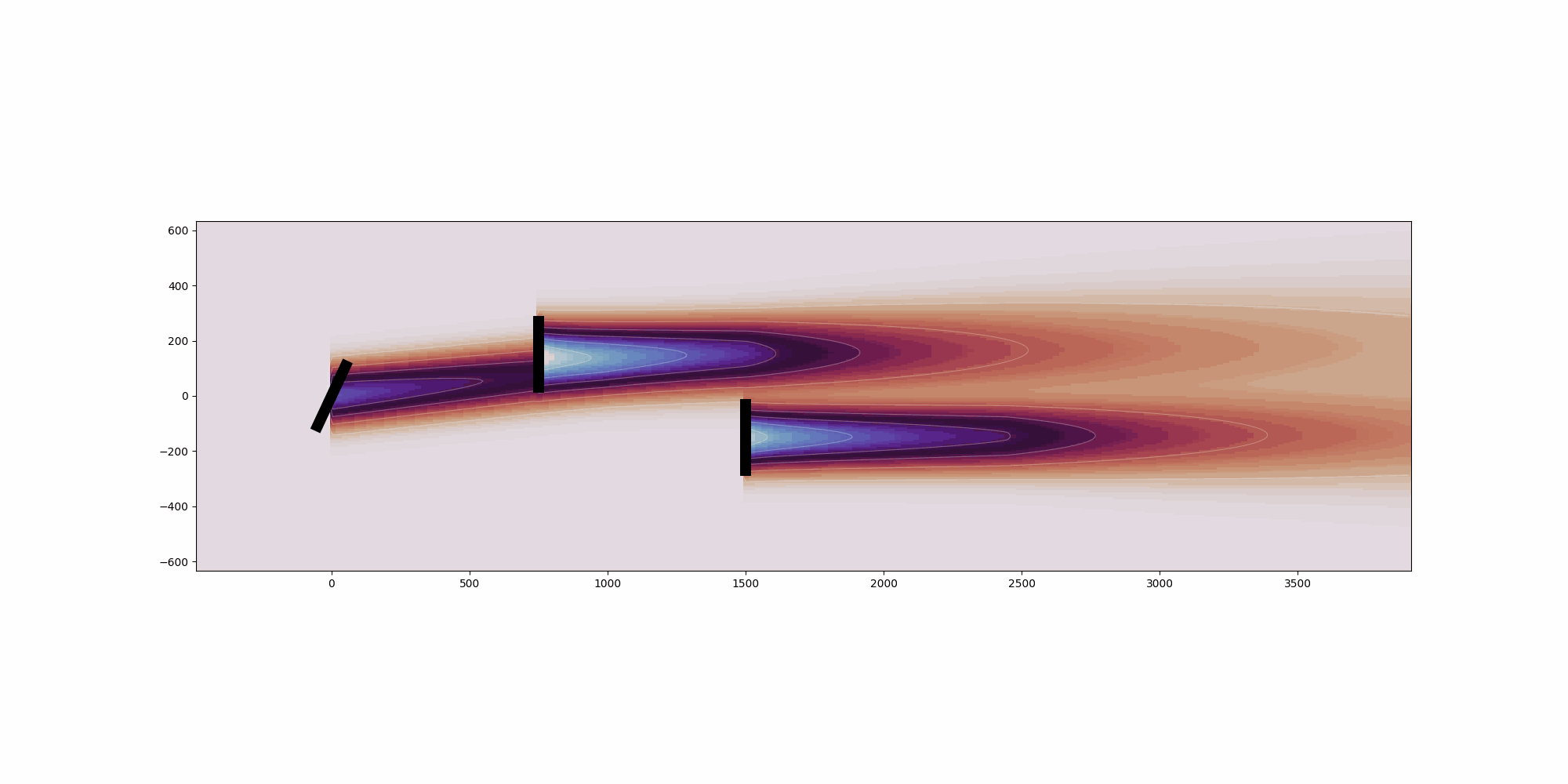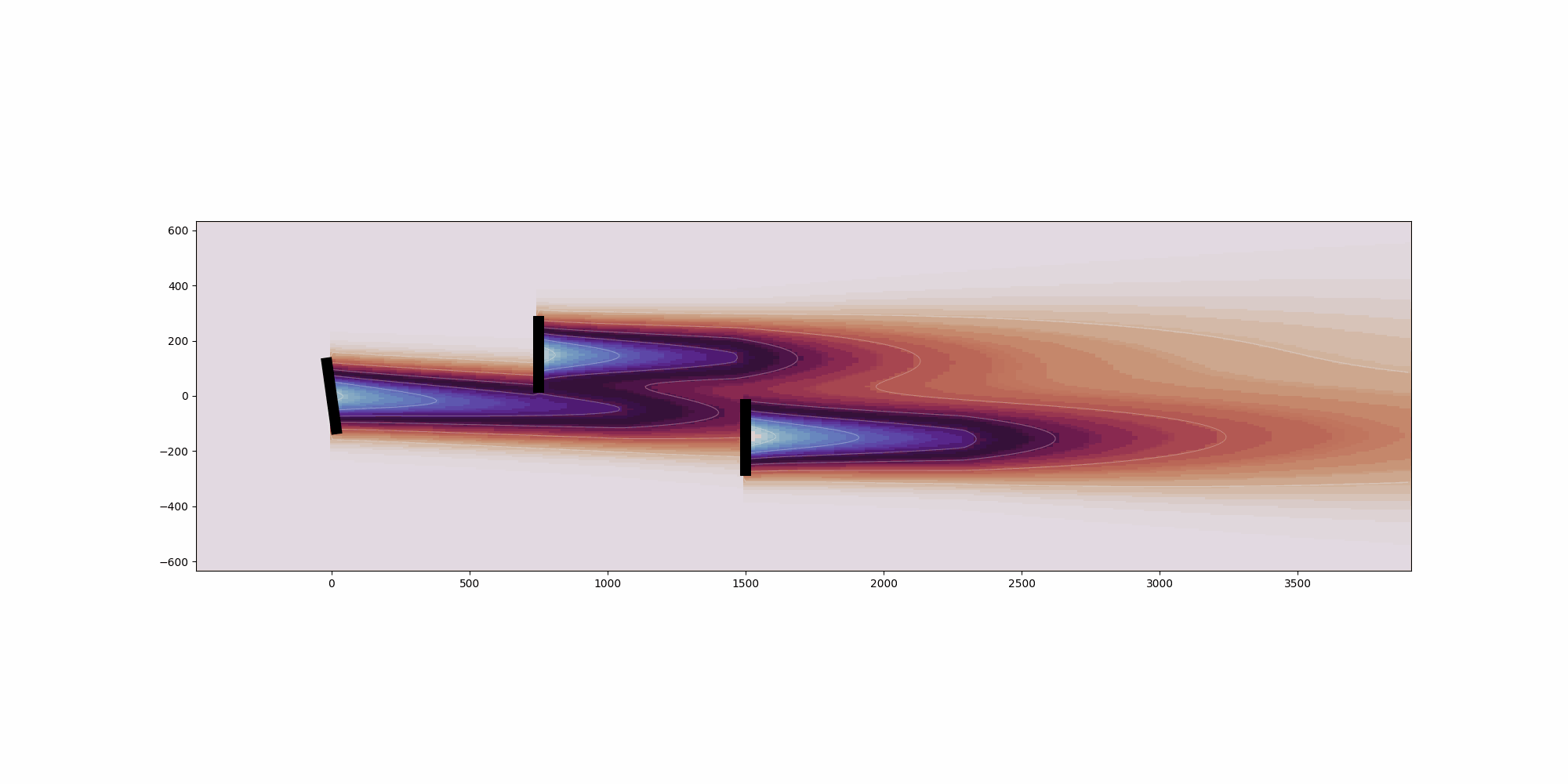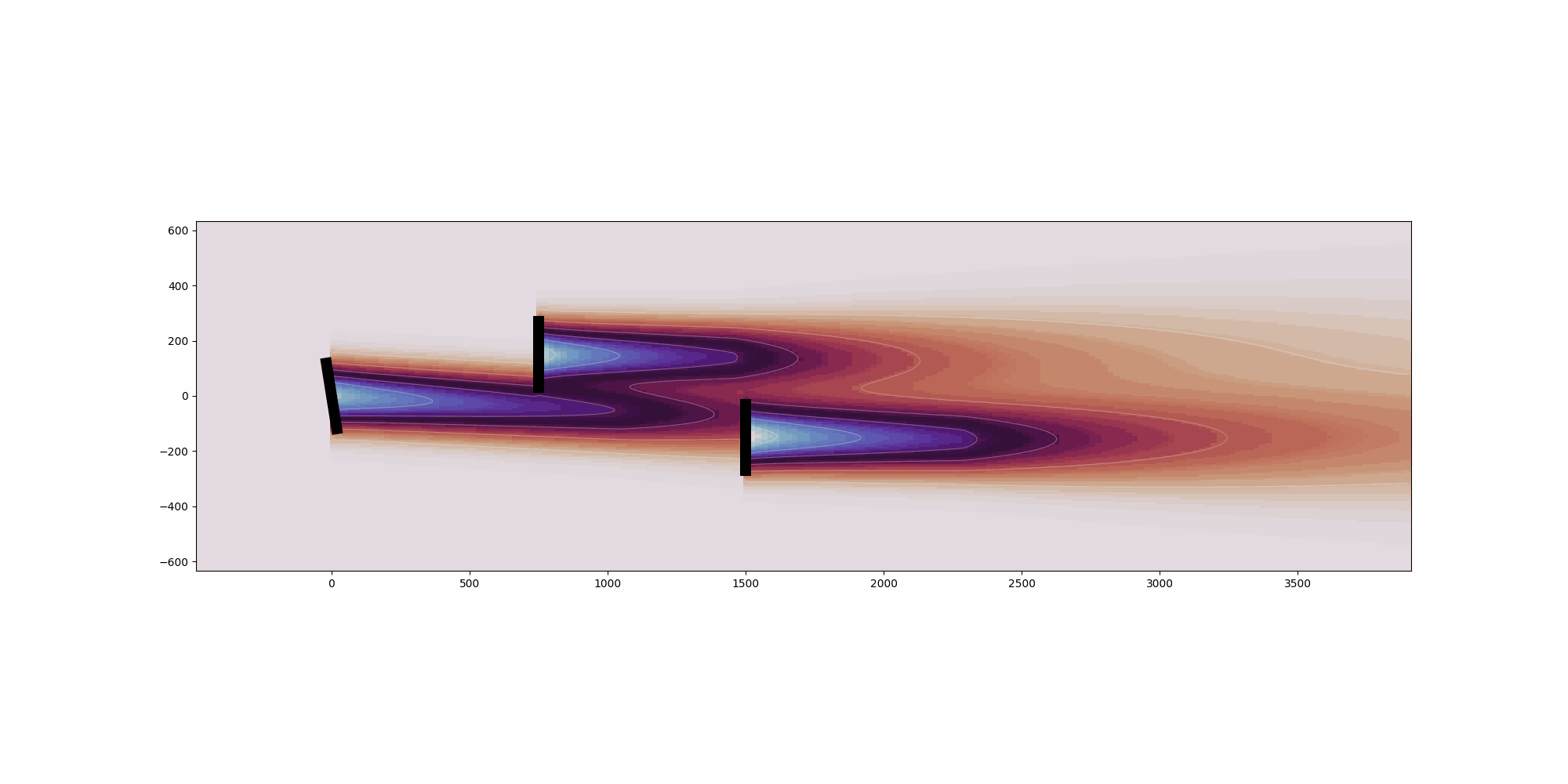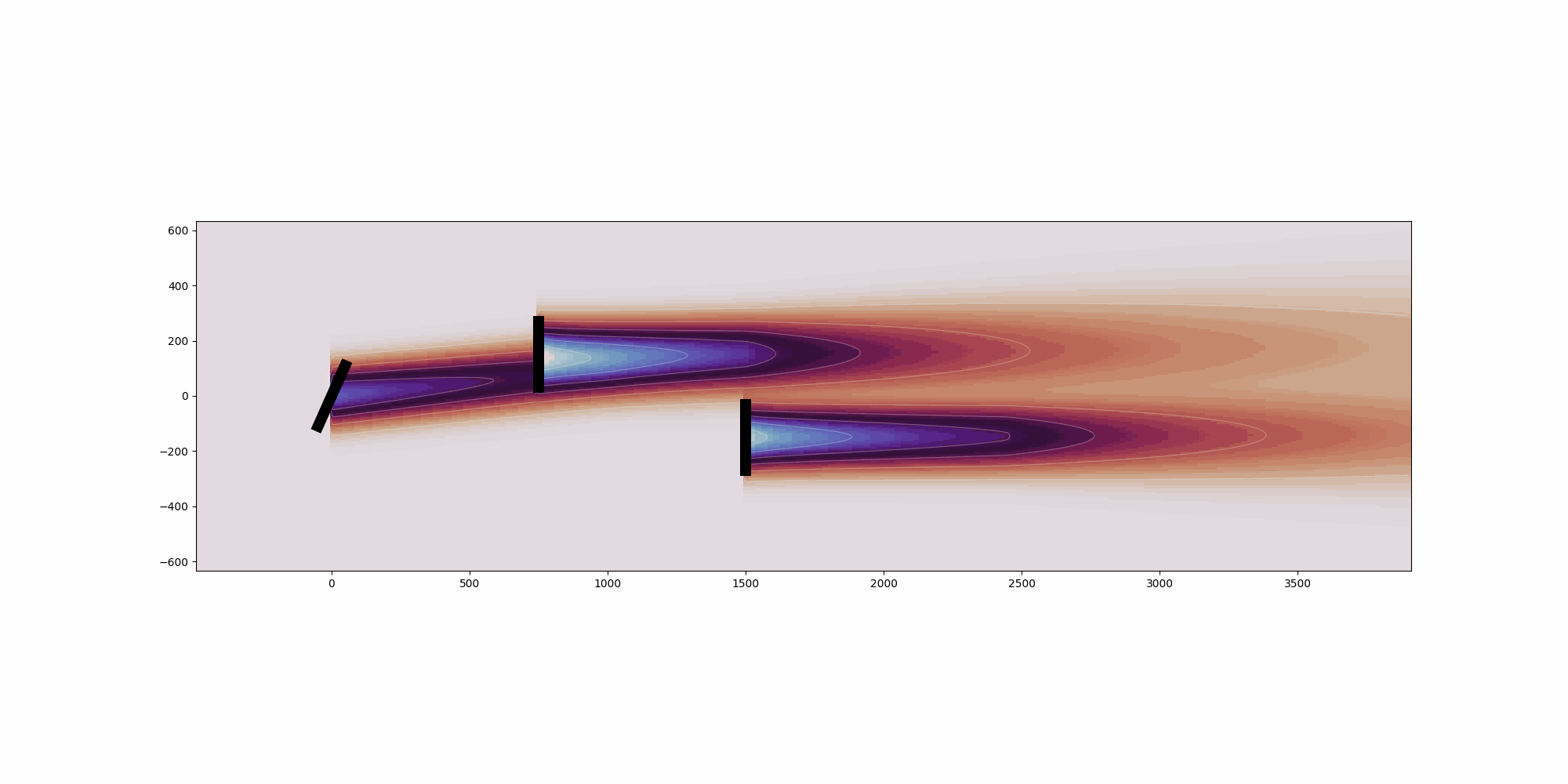
Calculates the deflection field of the wake. See
:cite:`gdm-bastankhah2016experimental` and :cite:`gdm-King2019Controls`
for details on the methods used.
Args:
x_i (np.array): x-coordinates of turbine i.
y_i (np.array): y-coordinates of turbine i.
yaw_i (np.array): Yaw angle of turbine i.
turbulence_intensity_i (np.array): Turbulence intensity at turbine i.
ct_i (np.array): Thrust coefficient of turbine i.
rotor_diameter_i (float): Rotor diameter of turbine i.
Returns:
np.array: Deflection field for the wake.
"""
# ==============================================================
# Opposite sign convention in this model
yaw_i *= -1
# TODO: connect support for tilt
tilt = 0.0 # turbine.tilt_angle
# initial velocity deficits
uR = (
freestream_velocity
* ct_i
* cosd(tilt)
* cosd(yaw_i)
/ (2.0 * (1 - np.sqrt(1 - (ct_i * cosd(tilt) * cosd(yaw_i)))))
)
u0 = freestream_velocity * np.sqrt(1 - ct_i)
# length of near wake
x0 = (
rotor_diameter_i
* (cosd(yaw_i) * (1 + np.sqrt(1 - ct_i * cosd(yaw_i))))
/ (np.sqrt(2) * (
4 * self.alpha * turbulence_intensity_i + 2 * self.beta * (1 - np.sqrt(1 - ct_i))
)) + x_i
)
# wake expansion parameters
ky = self.ka * turbulence_intensity_i + self.kb
kz = self.ka * turbulence_intensity_i + self.kb
C0 = 1 - u0 / freestream_velocity
M0 = C0 * (2 - C0)
E0 = ne.evaluate("C0 ** 2 - 3 * exp(1.0 / 12.0) * C0 + 3 * exp(1.0 / 3.0)")
# initial Gaussian wake expansion
sigma_z0 = ne.evaluate("rotor_diameter_i * 0.5 * sqrt(uR / (freestream_velocity + u0))")
sigma_y0 = sigma_z0 * cosd(yaw_i) * cosd(wind_veer)
# yR = y - y_i
xR = x_i # yR * tand(yaw) + x_i
# yaw parameters (skew angle and distance from centerline)
# skew angle in radians
theta_c0 = self.dm * (0.3 * np.radians(yaw_i) / cosd(yaw_i))
theta_c0 *= (1 - np.sqrt(1 - ct_i * cosd(yaw_i)))
delta0 = np.tan(theta_c0) * (x0 - x_i) # initial wake deflection;
# NOTE: use np.tan here since theta_c0 is radians
# deflection in the near wake
delta_near_wake = ((x - xR) / (x0 - xR)) * delta0 + (self.ad + self.bd * (x - x_i))
delta_near_wake *= (x >= xR) & (x <= x0)
# deflection in the far wake
sigma_y = ky * (x - x0) + sigma_y0
sigma_z = kz * (x - x0) + sigma_z0
sigma_y = sigma_y * (x >= x0) + sigma_y0 * (x < x0)
sigma_z = sigma_z * (x >= x0) + sigma_z0 * (x < x0)
M0_sqrt = np.sqrt(M0)
middle_term = np.sqrt(sigma_y * sigma_z / (sigma_y0 * sigma_z0))
ln_deltaNum = (1.6 + M0_sqrt) * (1.6 * middle_term - M0_sqrt)
ln_deltaDen = (1.6 - M0_sqrt) * (1.6 * middle_term + M0_sqrt)
middle_term = ne.evaluate(
"theta_c0"
" * E0"
" / 5.2"
" * sqrt(sigma_y0 * sigma_z0 / (ky * kz * M0))"
" * log(ln_deltaNum / ln_deltaDen)"
)
delta_far_wake = delta0 + middle_term + (self.ad + self.bd * (x - x_i))
delta_far_wake = delta_far_wake * (x > x0)
deflection = delta_near_wake + delta_far_wake
return deflection
## GCH components
[docs]
def gamma(
D,
velocity,
Uinf,
Ct,
scale=1.0,
):
"""
Vortex circulation strength. Units of XXX TODO
Args:
D (float): Rotor diameter of the current turbine
velocity (np.array(float)): Velocities at the current turbine
Uinf (float): Free-stream velocity
Ct (float): Thrust coefficient at the current turbine
Returns:
[type]: [description]
"""
# NOTE the cos commented below is included in Ct
return scale * (pi / 8) * D * velocity * Uinf * Ct # * cosd(yaw)
[docs]
def wake_added_yaw(
u_i,
v_i,
u_initial,
delta_y,
z_i,
rotor_diameter,
hub_height,
ct_i,
tip_speed_ratio,
axial_induction_i,
wind_shear,
scale=1.0,
):
"""
what yaw angle would have produced that same average spanwise velocity
These calculations focus around the current turbine. The formulation could
remove the dimension for n-turbines, but for consistency with other
similar equations it is left. However, the turbine dimension should
always have length 1.
"""
# turbine parameters
D = rotor_diameter # scalar
HH = hub_height # scalar
Ct = ct_i # (findex, 1, 1, 1) for the current turbine
TSR = tip_speed_ratio # scalar
aI = axial_induction_i # (findex, 1, 1, 1) for the current turbine
avg_v = np.mean(v_i, axis=(2,3)) # (findex, 1, grid, grid)
# flow parameters
Uinf = np.mean(u_initial, axis=(1, 2, 3))
Uinf = Uinf[:, None, None, None]
# TODO: Allow user input for eps gain
eps_gain = 0.2
eps = eps_gain * D # Use set value
vel_top = ((HH + D / 2) / HH) ** wind_shear * np.ones((1, 1, 1, 1))
Gamma_top = gamma(
D,
vel_top,
Uinf,
Ct,
scale,
)
vel_bottom = ((HH - D / 2) / HH) ** wind_shear * np.ones((1, 1, 1, 1))
Gamma_bottom = -1 * gamma(
D,
vel_bottom,
Uinf,
Ct,
scale,
)
turbine_average_velocity = np.cbrt(np.mean(u_i ** 3, axis=(2, 3)))[:, :, None, None]
Gamma_wake_rotation = 0.25 * 2 * pi * D * (aI - aI ** 2) * turbine_average_velocity / TSR
### compute the spanwise and vertical velocities induced by yaw
# decay = eps ** 2 / (4 * nu * delta_x / Uinf + eps ** 2) # This is the decay downstream
yLocs = delta_y + NUM_EPS
# top vortex
# NOTE: this is the top of the grid, not the top of the rotor
zT = z_i - (HH + D / 2) + NUM_EPS # distance from the top of the grid
rT = ne.evaluate("yLocs ** 2 + zT ** 2") # TODO: This is (-) in the paper
# This looks like spanwise decay;
# it defines the vortex profile in the spanwise directions
core_shape = ne.evaluate("1 - exp(-rT / (eps ** 2))")
v_top = ne.evaluate("(Gamma_top * zT) / (2 * pi * rT) * core_shape")
v_top = np.mean( v_top, axis=(2,3) )
# w_top = (-1 * Gamma_top * yLocs) / (2 * pi * rT) * core_shape * decay
# bottom vortex
zB = z_i - (HH - D / 2) + NUM_EPS
rB = ne.evaluate("yLocs ** 2 + zB ** 2")
core_shape = ne.evaluate("1 - exp(-rB / (eps ** 2))")
v_bottom = ne.evaluate("(Gamma_bottom * zB) / (2 * pi * rB) * core_shape")
v_bottom = np.mean( v_bottom, axis=(2,3) )
# w_bottom = (-1 * Gamma_bottom * yLocs) / (2 * pi * rB) * core_shape * decay
# wake rotation vortex
zC = z_i - HH + NUM_EPS
rC = ne.evaluate("yLocs ** 2 + zC ** 2")
core_shape = ne.evaluate("1 - exp(-rC / (eps ** 2))")
v_core = ne.evaluate("(Gamma_wake_rotation * zC) / (2 * pi * rC) * core_shape")
v_core = np.mean( v_core, axis=(2,3) )
# w_core = (-1 * Gamma_wake_rotation * yLocs) / (2 * pi * rC) * core_shape * decay
# Cap the effective yaw values between -45 and 45 degrees
val = 2 * (avg_v - v_core) / (v_top + v_bottom)
val = np.where(val < -1.0, -1.0, val)
val = np.where(val > 1.0, 1.0, val)
y = np.degrees(0.5 * np.arcsin(val))
return y[:, :, None, None]
[docs]
def calculate_transverse_velocity(
u_i,
u_initial,
dudz_initial,
delta_x,
delta_y,
z,
rotor_diameter,
hub_height,
yaw,
ct_i,
tsr_i,
axial_induction_i,
wind_shear,
scale=1.0,
):
"""
Calculate transverse velocity components for all downstream turbines
given the vortices at the current turbine.
"""
# turbine parameters
D = rotor_diameter
HH = hub_height
Ct = ct_i
TSR = tsr_i
aI = axial_induction_i
# flow parameters
Uinf = np.mean(u_initial, axis=(1, 2, 3))
Uinf = Uinf[:, None, None, None]
eps_gain = 0.2
eps = eps_gain * D # Use set value
vel_top = ((HH + D / 2) / HH) ** wind_shear * np.ones((1, 1, 1, 1))
Gamma_top = sind(yaw) * cosd(yaw) * gamma(
D,
vel_top,
Uinf,
Ct,
scale,
)
vel_bottom = ((HH - D / 2) / HH) ** wind_shear * np.ones((1, 1, 1, 1))
Gamma_bottom = -1 * sind(yaw) * cosd(yaw) * gamma(
D,
vel_bottom,
Uinf,
Ct,
scale,
)
turbine_average_velocity = np.cbrt(np.mean(u_i ** 3, axis=(2,3)))[:, :, None, None]
Gamma_wake_rotation = 0.25 * 2 * pi * D * (aI - aI ** 2) * turbine_average_velocity / TSR
### compute the spanwise and vertical velocities induced by yaw
# decay the vortices as they move downstream - using mixing length
lmda = D / 8
kappa = 0.41
lm = kappa * z / (1 + kappa * z / lmda)
nu = lm ** 2 * np.abs(dudz_initial)
# This is the decay downstream
decay = ne.evaluate("eps ** 2 / (4 * nu * delta_x / Uinf + eps ** 2)")
yLocs = delta_y + NUM_EPS
# top vortex
zT = z - (HH + D / 2) + NUM_EPS
rT = ne.evaluate("yLocs ** 2 + zT ** 2") # TODO: This is - in the paper
# This looks like spanwise decay;
# it defines the vortex profile in the spanwise directions
core_shape = ne.evaluate("1 - exp(-rT / (eps ** 2))")
V1 = ne.evaluate("(Gamma_top * zT) / (2 * pi * rT) * core_shape * decay")
W1 = ne.evaluate("(-1 * Gamma_top * yLocs) / (2 * pi * rT) * core_shape * decay")
# bottom vortex
zB = z - (HH - D / 2) + NUM_EPS
rB = ne.evaluate("yLocs ** 2 + zB ** 2")
core_shape = ne.evaluate("1 - exp(-rB / (eps ** 2))")
V2 = ne.evaluate("(Gamma_bottom * zB) / (2 * pi * rB) * core_shape * decay")
W2 = ne.evaluate("(-1 * Gamma_bottom * yLocs) / (2 * pi * rB) * core_shape * decay")
# wake rotation vortex
zC = z - HH + NUM_EPS
rC = ne.evaluate("yLocs ** 2 + zC ** 2")
core_shape = ne.evaluate("1 - exp(-rC / (eps ** 2))")
V5 = ne.evaluate("(Gamma_wake_rotation * zC) / (2 * pi * rC) * core_shape * decay")
W5 = ne.evaluate("(-1 * Gamma_wake_rotation * yLocs) / (2 * pi * rC) * core_shape * decay")
### Boundary condition - ground mirror vortex
# top vortex - ground
zTb = z + (HH + D / 2) + NUM_EPS
rTb = ne.evaluate("yLocs ** 2 + zTb ** 2")
# This looks like spanwise decay;
# it defines the vortex profile in the spanwise directions
core_shape = ne.evaluate("1 - exp(-rTb / (eps ** 2))")
V3 = ne.evaluate("(-1 * Gamma_top * zTb) / (2 * pi * rTb) * core_shape * decay")
W3 = ne.evaluate("(Gamma_top * yLocs) / (2 * pi * rTb) * core_shape * decay")
# bottom vortex - ground
zBb = z + (HH - D / 2) + NUM_EPS
rBb = ne.evaluate("yLocs ** 2 + zBb ** 2")
core_shape = ne.evaluate("1 - exp(-rBb / (eps ** 2))")
V4 = ne.evaluate("(-1 * Gamma_bottom * zBb) / (2 * pi * rBb) * core_shape * decay")
W4 = ne.evaluate("(Gamma_bottom * yLocs) / (2 * pi * rBb) * core_shape * decay")
# wake rotation vortex - ground effect
zCb = z + HH + NUM_EPS
rCb = ne.evaluate("yLocs ** 2 + zCb ** 2")
core_shape = ne.evaluate("1 - exp(-rCb / (eps ** 2))")
V6 = ne.evaluate("(-1 * Gamma_wake_rotation * zCb) / (2 * pi * rCb) * core_shape * decay")
W6 = ne.evaluate("(Gamma_wake_rotation * yLocs) / (2 * pi * rCb) * core_shape * decay")
# total spanwise velocity
V = V1 + V2 + V3 + V4 + V5 + V6
W = W1 + W2 + W3 + W4 + W5 + W6
# No spanwise and vertical velocity upstream of the turbine
### Original v3 implementation
# V[delta_x < -1] = 0.0 # Subtract by 1 to avoid numerical issues on rotation
# W[delta_x < -1] = 0.0 # Subtract by 1 to avoid numerical issues on rotation
# TODO Should this be <= ? Shouldn't be adding V and W on the current turbine?
### Then we changed it to this
# V[delta_x < 0.0] = 0.0 # Subtract by 1 to avoid numerical issues on rotation
# W[delta_x < 0.0] = 0.0 # Subtract by 1 to avoid numerical issues on rotation
### Currently, here
V = np.where(delta_x >= 0.0, V, 0.0)
W = np.where(delta_x >= 0.0, W, 0.0)
# TODO: Why would the say W cannot be negative?
W = np.where(W >= 0, W, 0.0)
return V, W
[docs]
def yaw_added_turbulence_mixing(
u_i,
I_i,
v_i,
w_i,
turb_v_i,
turb_w_i
):
# Since turbulence mixing is constant for the turbine,
# use the left two dimensions only here and expand
# before returning. Dimensions are (wd, ws).
I_i = I_i[:, 0, 0, 0]
average_u_i = np.cbrt(np.mean(u_i ** 3, axis=(1, 2, 3)))
# Convert ambient turbulence intensity to TKE (eq 24)
k = (average_u_i * I_i) ** 2 / (2 / 3)
u_term = np.sqrt(2 * k)
v_term = np.mean(v_i + turb_v_i, axis=(1, 2, 3))
w_term = np.mean(w_i + turb_w_i, axis=(1, 2, 3))
# Compute the new TKE (eq 23)
k_total = 0.5 * (u_term ** 2 + v_term ** 2 + w_term ** 2)
# Convert TKE back to TI
I_total = np.sqrt((2 / 3) * k_total) / average_u_i
# Remove ambient from total TI leaving only the TI due to mixing
I_mixing = I_total - I_i
return I_mixing[:, None, None, None]